What Is Linear Economy
A linear economy is the traditional “take-make-waste” model where raw materials are collected and transformed into products that are used until they are finally discarded as waste. Value is created in this economic system by producing and selling as many products as possible.
What Is Circular Economy
A circular economy is an economic system aimed at eliminating waste and the continual use of resources. It is an alternative to the traditional linear economy.
In the context of a circular economy, we keep resources in use for as long as possible, extract the maximum value from them whilst in use, then recover and regenerate products and materials at the end of each service life.

3 Advantages of Circular Economy
1) Reduce Environmental Damage
Extracting less raw materials or using less fossil energy will lead to smaller waste disposal problems.
2) Decent Jobs and Economic Growth
Eco-industry has the potential to generate innovations and new employment opportunities due to the development and application of technology.
In processes labelled as ‘local mining’, ‘near sourcing’ or ‘reshoring’, jobs could be shifted back to local people and contribute to local economic growth, rather than current outsourcing practice.
3) Reliability on Supply Chain
With advancement in production processes that require less newly produced or mined raw materials, these processes become less sensitive to the growing scarcity of many raw materials. Geopolitical wise, conditions of supplying countries will have less influence on consuming countries.
Further readings:
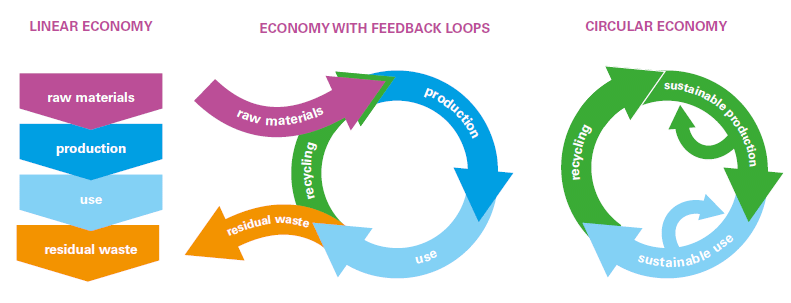
If you would like to know further about the differences, characterizing linear economy, economy with feedback loops, and circular economy (RLi, 2015) Van Buren et al. (2016) summarize the potential, and in some cases already proven, advantages of the circular economy approach in terms of three major categories. Read more at Research Gate.



